Multi-Modal Human-Swarm Interaction Using Vision, Speech & Multi-Agent LLMs
 Multi-Agent LLM-based Swarm Robots
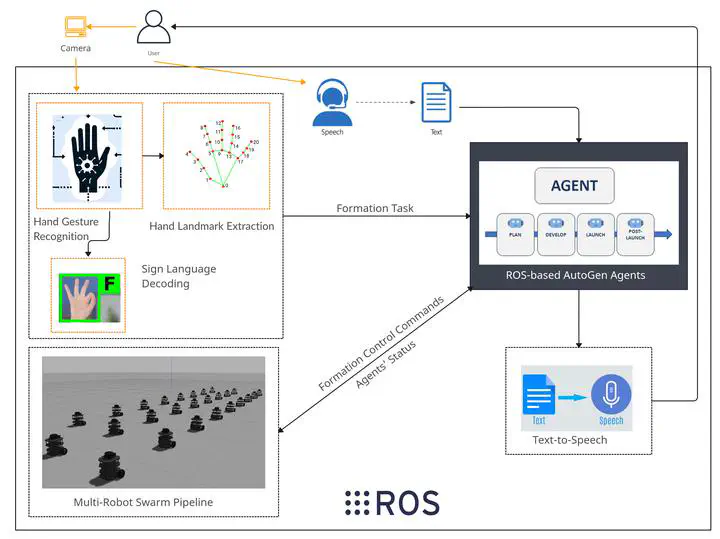
Multi-Agent LLM-based Swarm RobotsProject Overview: Our team of two master’s students embarked on a groundbreaking project at the University of Zagreb, aimed at revolutionizing Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) by integrating computer vision, speech recognition, and multi-agent Large Language Models (LLMs). We developed a sophisticated system that interprets human gestures, text, and verbal commands to dynamically control a swarm of robots, making interaction more intuitive and efficient.
Innovative Contributions:
- Implemented a cutting-edge system combining Google’s MediaPipe for gesture recognition and Microsoft’s AutoGen conversational multi-agents, alongside speech recognition technologies.
- Pioneered the integration of LLMs to process complex commands and facilitate direct, natural language interaction between humans and robot swarms.
- Demonstrated the system’s versatility through rigorous testing, showcasing its capability to perform intricate swarm formations and respond to diverse user commands in real-time.
Technical and Research Impact: Our research represents a significant leap forward in HRI, enabling seamless communication with robotic swarms using natural human behaviors. This project not only showcases the potential of multi-modal interfaces in enhancing swarm robotics but also contributes valuable insights into the practical application of LLMs in robotic systems. The successful implementation and testing in simulated environments underscore the feasibility and effectiveness of our approach, with implications for future real-world applications in areas such as search and rescue, surveillance, and environmental monitoring.
Personal Contributions and Skills Development: I played a pivotal role in the design and implementation of the system’s architecture, focusing on the integration of gesture and speech recognition modules with LLM agents. My contributions extended to conducting extensive simulations, analyzing system performance, and co-authoring the project report. This project has significantly enhanced my expertise in robotics, machine learning, and software engineering, preparing me for a future at the forefront of technological innovation.
Looking Forward: Our findings lay the groundwork for further research into real-world deployment and the exploration of additional modalities for human-swarm interaction. Future work will explore the embodiment of LLMs in individual robots and the application of our system to practical tasks, aiming to reduce cognitive load on users and enhance the autonomy and decision-making capabilities of robotic swarms.
Conclusion: This project not only showcased my ability to conceptualize exciting and innovative ideas in the field of robotics but also demonstrated my drive to bring such ideas to fruition. Our work’s significance, particularly in integrating LLMs for intuitive control, positions us at the cutting edge of research, paving the way for future developments that promise to transform the interaction between humans and robotic systems.